Publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2026
- AAAI26
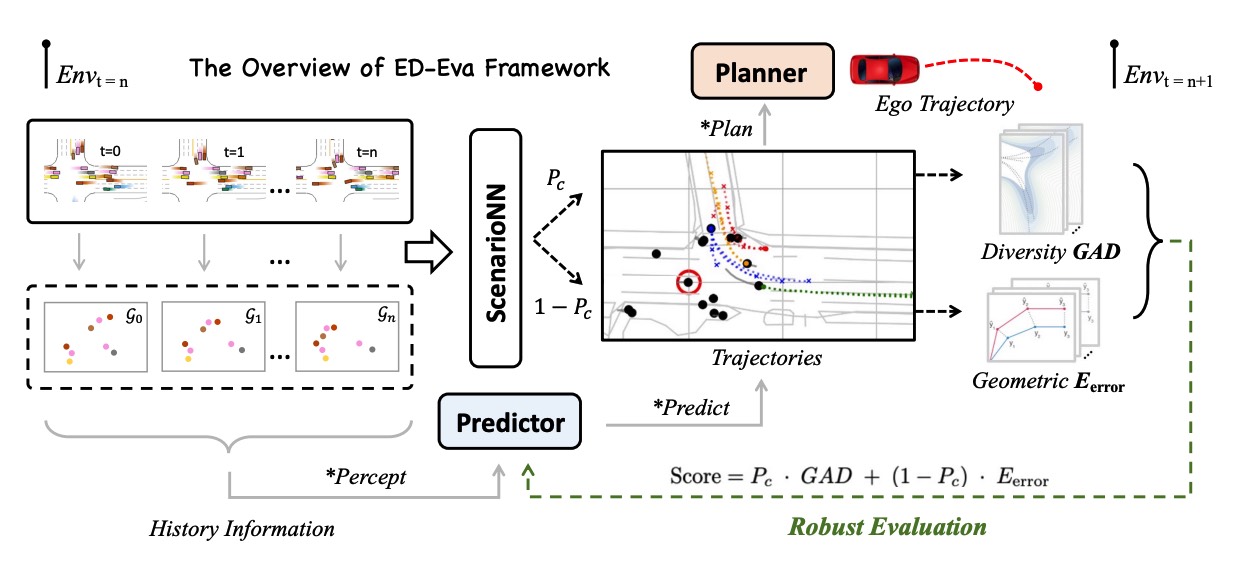 Measuring What Matters: Scenario-Driven Evaluation for Trajectory Predictors in Autonomous DrivingLongchao Da, David Isele, Hua Wei , and 1 more author2026
Measuring What Matters: Scenario-Driven Evaluation for Trajectory Predictors in Autonomous DrivingLongchao Da, David Isele, Hua Wei , and 1 more author2026Being able to anticipate the motion of surrounding agents is essential for the safe operation of autonomous driving systems in dynamic situations. While various methods have been proposed for trajectory prediction, the current evaluation practices still rely on error-based metrics (e.g., ADE, FDE), which reveal the accuracy from a post-hoc view but ignore the actual effect the predictor brings to the self-driving vehicles (SDVs), especially in complex interactive scenarios: a high-quality predictor not only chases accuracy, but should also captures all possible directions a neighbor agent might move, to support the SDVs’ cautious decision-making. Given that the existing metrics hardly account for this standard, in our work, we propose a comprehensive pipeline that adaptively evaluates the predictor’s performance by two dimensions: accuracy and diversity. Based on the criticality of the driving scenario, these two dimensions are dynamically combined and result in a final score for the predictor’s performance. Extensive experiments on a closed-loop benchmark using a real-world dataset show that our pipeline yields a more reasonable evaluation than traditional metrics by better reflecting the correlation of the predictors’ evaluation with the autonomous vehicles’ driving performance. This evaluation pipeline shows a robust way to select a predictor that potentially contributes most to the SDV’s driving performance. The code and dataset are provided in the supplementary material.
@article{longchao, title = {Measuring What Matters: Scenario-Driven Evaluation for Trajectory Predictors in Autonomous Driving}, author = {Da, Longchao and Isele, David and Wei, Hua and Saroya, Manish}, year = {2026}, }
2025
- KDD25
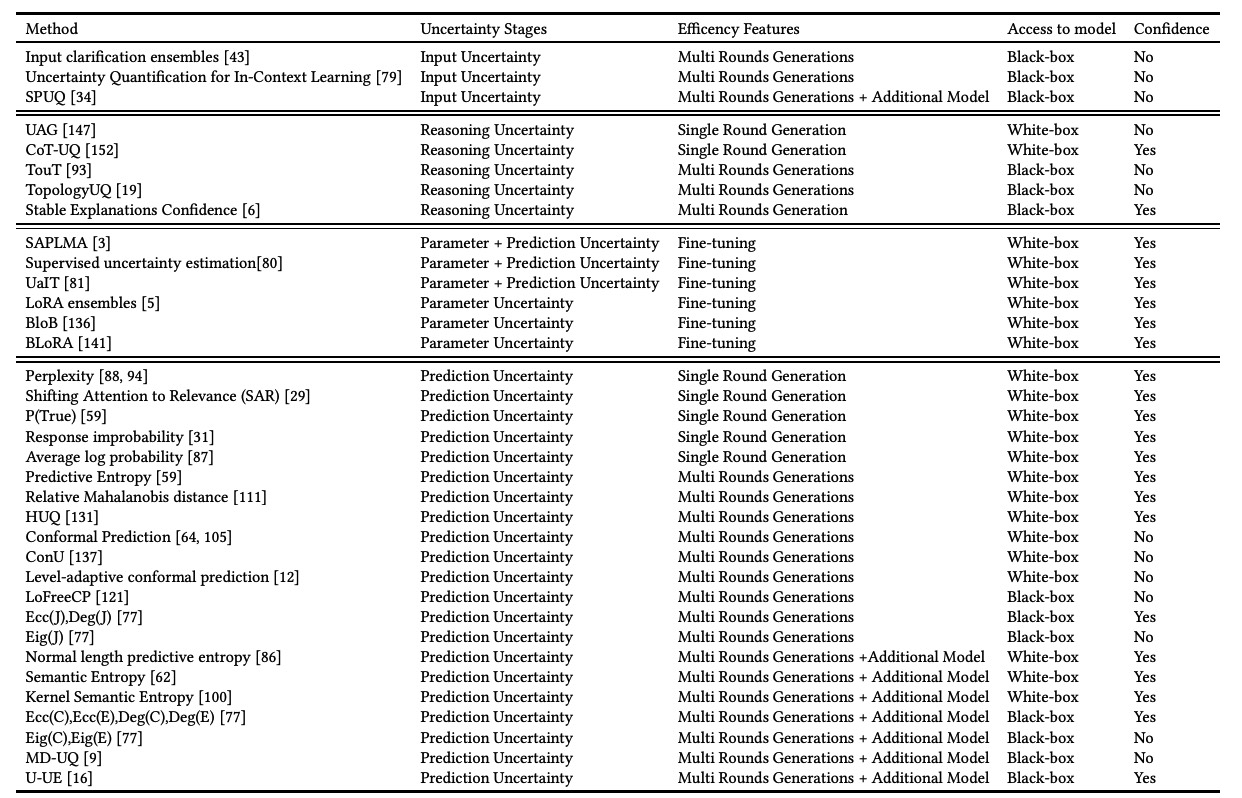 Uncertainty Quantification and Confidence Calibration in Large Language Models: A SurveyXiaoou Liu, Tiejin Chen, Longchao Da , and 3 more authors2025
Uncertainty Quantification and Confidence Calibration in Large Language Models: A SurveyXiaoou Liu, Tiejin Chen, Longchao Da , and 3 more authors2025Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in text generation, reasoning, and decision-making, enabling their adoption in high-stakes domains such as healthcare, law, and transportation. However, their reliability is a major concern, as they often produce plausible but incorrect responses. Uncertainty quantification (UQ) enhances trustworthiness by estimating confidence in outputs, enabling risk mitigation and selective prediction. However, traditional UQ methods struggle with LLMs due to computational constraints and decoding inconsistencies. Moreover, LLMs introduce unique uncertainty sources, such as input ambiguity, reasoning path divergence, and decoding stochasticity, that extend beyond classical aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty. To address this, we introduce a new taxonomy that categorizes UQ methods based on computational efficiency and uncertainty dimensions (input, reasoning, parameter, and prediction uncertainty). We evaluate existing techniques, assess their real-world applicability, and identify open challenges, emphasizing the need for scalable, interpretable, and robust UQ approaches to enhance LLM reliability.
@article{liu2025uncertainty, title = {Uncertainty Quantification and Confidence Calibration in Large Language Models: A Survey}, author = {Liu, Xiaoou and Chen, Tiejin and Da, Longchao and Chen, Chacha and Lin, Zhen and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - COLM25
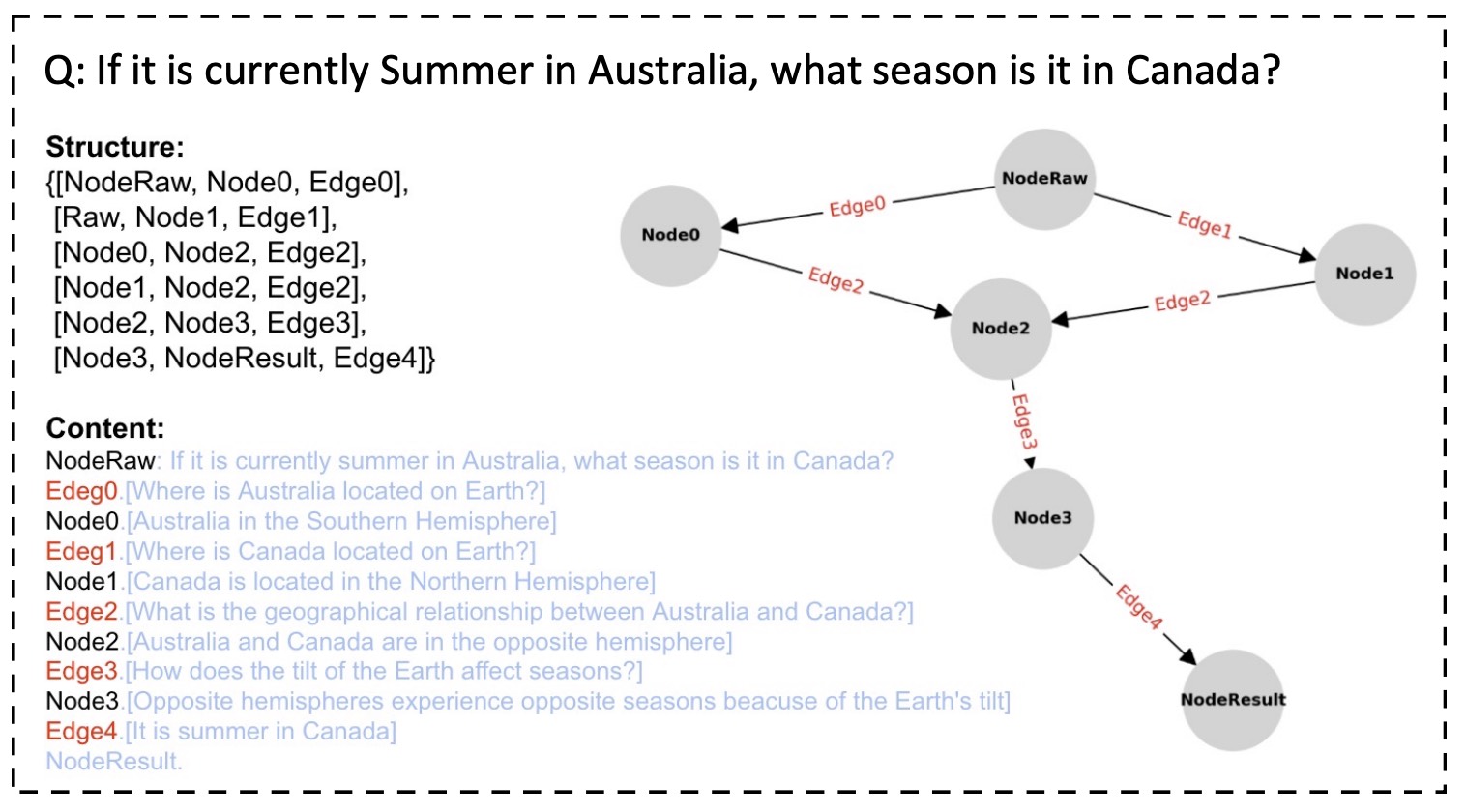 Understanding the Uncertainty of LLM Explanations: A Perspective Based on Reasoning TopologyLongchao Da, Xiaoou Liu, Jiaxin Dai , and 3 more authors2025
Understanding the Uncertainty of LLM Explanations: A Perspective Based on Reasoning TopologyLongchao Da, Xiaoou Liu, Jiaxin Dai , and 3 more authors2025Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various tasks due to large training datasets and powerful transformer architecture. However, the reliability of responses from LLMs remains a question. Uncertainty quantification (UQ) of LLMs is crucial for ensuring their reliability, especially in areas such as healthcare, finance, and decision-making. Existing UQ methods primarily focus on semantic similarity, overlooking the deeper knowledge dimensions embedded in responses. We introduce a multi-dimensional UQ framework that integrates semantic and knowledge-aware similarity analysis. By generating multiple responses and leveraging auxiliary LLMs to extract implicit knowledge, we construct separate similarity matrices and apply tensor decomposition to derive a comprehensive uncertainty representation. This approach disentangles overlapping information from both semantic and knowledge dimensions, capturing both semantic variations and factual consistency, leading to more accurate UQ. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate that our method outperforms existing techniques in identifying uncertain responses, offering a more robust framework for enhancing LLM reliability in high-stakes applications.
@article{da2025understanding, title = {Understanding the Uncertainty of LLM Explanations: A Perspective Based on Reasoning Topology}, author = {Da, Longchao and Liu, Xiaoou and Dai, Jiaxin and Cheng, Lu and Wang, Yaqing and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - pre-print
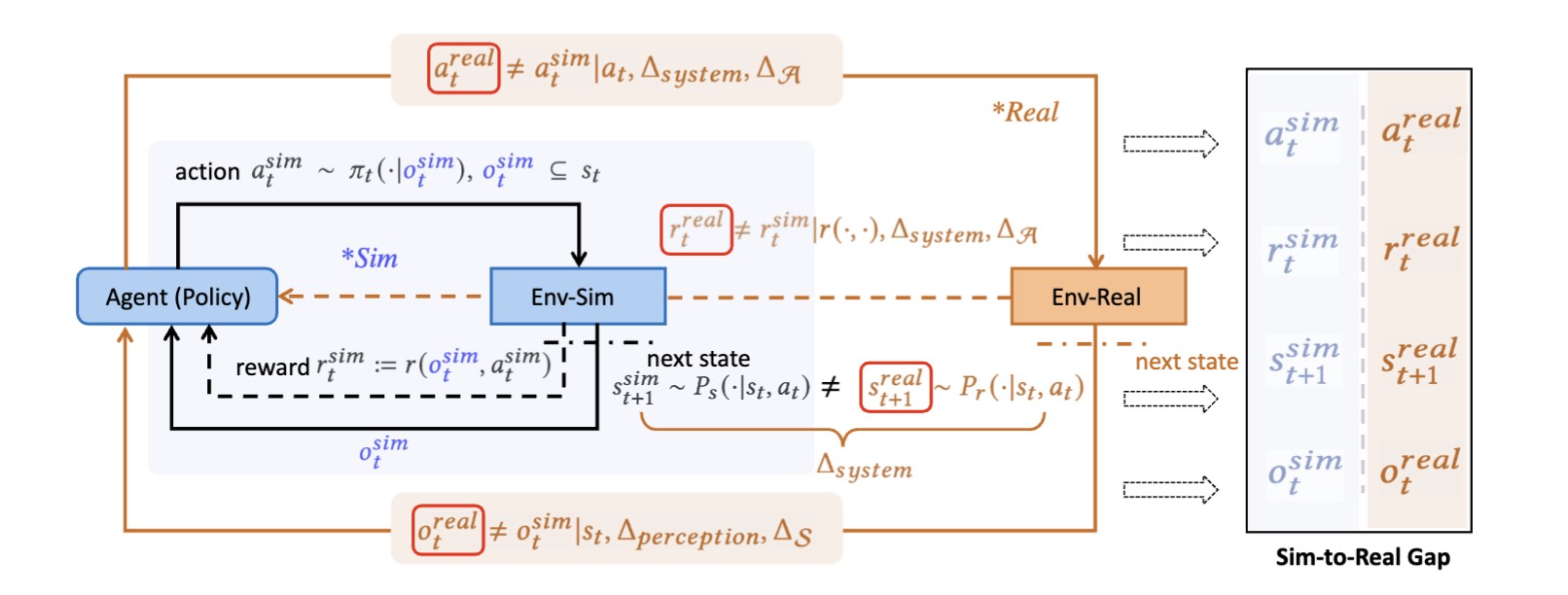 A Survey of Sim-to-Real Methods in RL: Progress, Prospects and Challenges with Foundation ModelsLongchao Da, Justin Turnau, Thirulogasankar Pranav Kutralingam , and 3 more authors2025
A Survey of Sim-to-Real Methods in RL: Progress, Prospects and Challenges with Foundation ModelsLongchao Da, Justin Turnau, Thirulogasankar Pranav Kutralingam , and 3 more authors2025Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) has been explored and verified to be effective in solving decision-making tasks in various domains, such as robotics, transportation, recommender systems, etc. It learns from the interaction with environments and updates the policy using the collected experience. However, due to the limited real-world data and unbearable consequences of taking detrimental actions, the learning of RL policy is mainly restricted within the simulators. This practice guarantees safety in learning but introduces an inevitable sim-to-real gap in terms of deployment, thus causing degraded performance and risks in execution. There are attempts to solve the sim-to-real problems from different domains with various techniques, especially in the era with emerging techniques such as large foundations or language models that have cast light on the sim-to-real. This survey paper, to the best of our knowledge, is the first taxonomy that formally frames the sim-to-real techniques from key elements of the Markov Decision Process (State, Action, Transition, and Reward). Based on the framework, we cover comprehensive literature from the classic to the most advanced methods including the sim-to-real techniques empowered by foundation models, and we also discuss the specialties that are worth attention in different domains of sim-to-real problems. Then we summarize the formal evaluation process of sim-to-real performance with accessible code or benchmarks. The challenges and opportunities are also presented to encourage future exploration of this direction. We are actively maintaining a to include the most up-to-date sim-to-real research outcomes to help the researchers in their work.
@article{da2025survey, title = {A Survey of Sim-to-Real Methods in RL: Progress, Prospects and Challenges with Foundation Models}, author = {Da, Longchao and Turnau, Justin and Kutralingam, Thirulogasankar Pranav and Velasquez, Alvaro and Shakarian, Paulo and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - pre-print
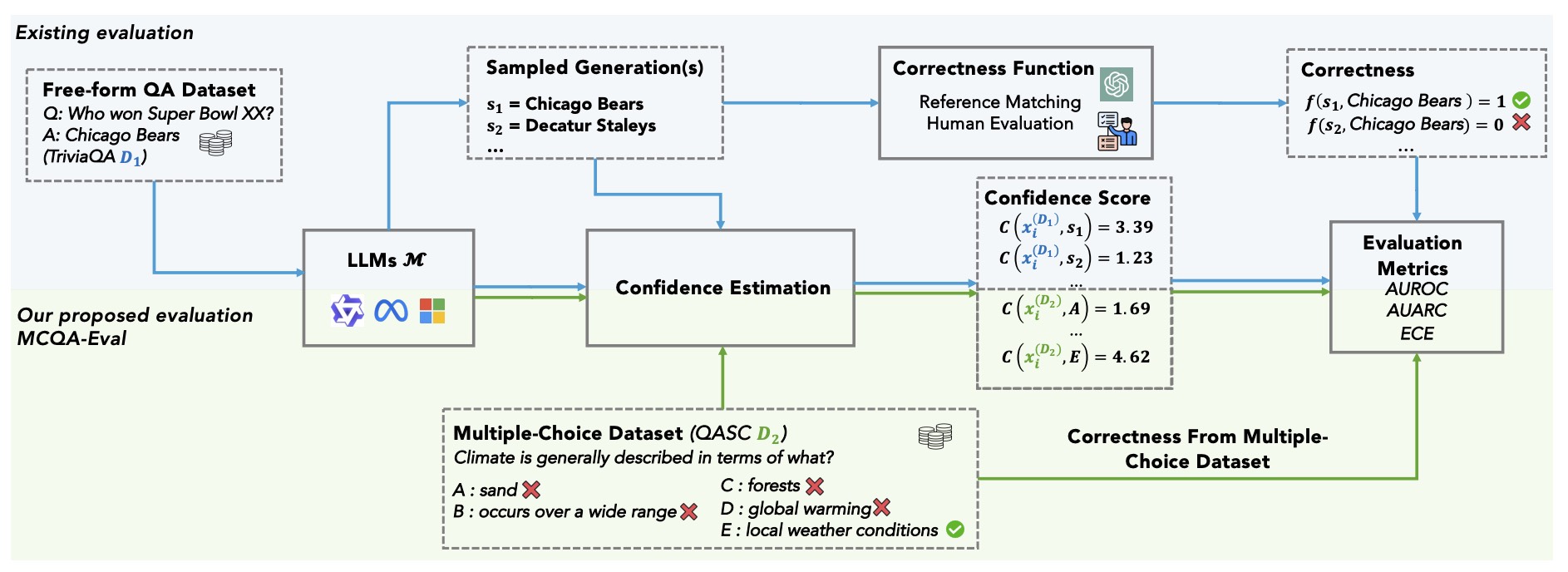 MCQA-Eval: Efficient Confidence Evaluation in NLG with Gold-Standard Correctness LabelsXiaoou Liu, Zhen Lin, Longchao Da , and 3 more authors2025
MCQA-Eval: Efficient Confidence Evaluation in NLG with Gold-Standard Correctness LabelsXiaoou Liu, Zhen Lin, Longchao Da , and 3 more authors2025Large Language Models (LLMs) require robust confidence estimation, particularly in critical domains like healthcare and law where unreliable outputs can lead to significant consequences. Despite much recent work in confidence estimation, current evaluation frameworks rely on correctness functions – various heuristics that are often noisy, expensive, and possibly introduce systematic biases. These methodological weaknesses tend to distort evaluation metrics and thus the comparative ranking of confidence measures. We introduce MCQA-Eval, an evaluation framework for assessing confidence measures in Natural Language Generation (NLG) that eliminates dependence on an explicit correctness function by leveraging gold-standard correctness labels from multiple-choice datasets. MCQA-Eval enables systematic comparison of both internal state-based white-box (e.g. logit-based) and consistency-based black-box confidence measures, providing a unified evaluation methodology across different approaches. Through extensive experiments on multiple LLMs and widely used QA datasets, we report that MCQA-Eval provides efficient and more reliable assessments of confidence estimation methods than existing approaches.
@article{liu2025mcqa, title = {MCQA-Eval: Efficient Confidence Evaluation in NLG with Gold-Standard Correctness Labels}, author = {Liu, Xiaoou and Lin, Zhen and Da, Longchao and Chen, Chacha and Trivedi, Shubhendu and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - pre-print
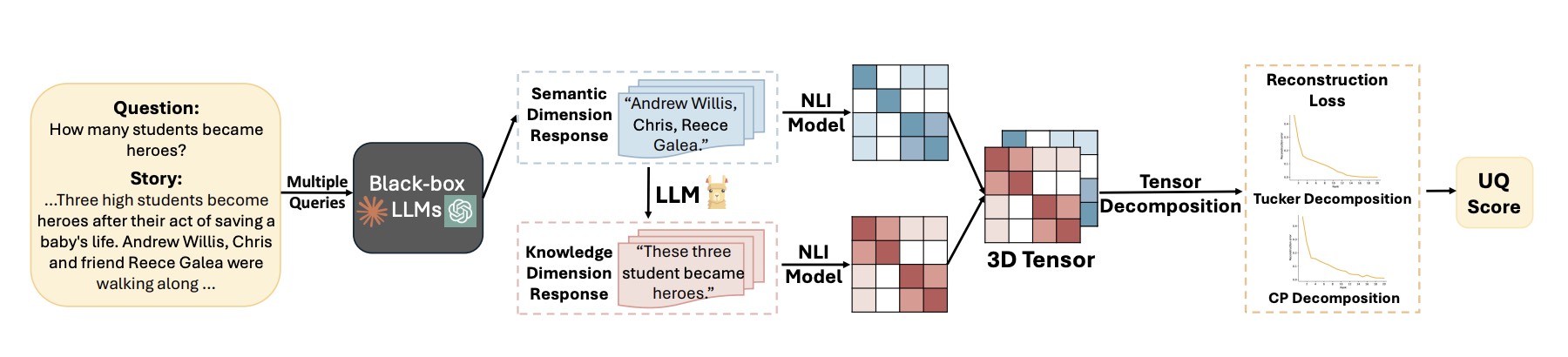 Uncertainty Quantification of Large Language Models through Multi-Dimensional ResponsesTiejin Chen, Xiaoou Liu, Longchao Da , and 2 more authors2025
Uncertainty Quantification of Large Language Models through Multi-Dimensional ResponsesTiejin Chen, Xiaoou Liu, Longchao Da , and 2 more authors2025Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various tasks due to large training datasets and powerful transformer architecture. However, the reliability of responses from LLMs remains a question. Uncertainty quantification (UQ) of LLMs is crucial for ensuring their reliability, especially in areas such as healthcare, finance, and decision-making. Existing UQ methods primarily focus on semantic similarity, overlooking the deeper knowledge dimensions embedded in responses. We introduce a multi-dimensional UQ framework that integrates semantic and knowledge-aware similarity analysis. By generating multiple responses and leveraging auxiliary LLMs to extract implicit knowledge, we construct separate similarity matrices and apply tensor decomposition to derive a comprehensive uncertainty representation. This approach disentangles overlapping information from both semantic and knowledge dimensions, capturing both semantic variations and factual consistency, leading to more accurate UQ. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate that our method outperforms existing techniques in identifying uncertain responses, offering a more robust framework for enhancing LLM reliability in high-stakes applications.
@article{chen2025uncertainty, title = {Uncertainty Quantification of Large Language Models through Multi-Dimensional Responses}, author = {Chen, Tiejin and Liu, Xiaoou and Da, Longchao and Papalexakis, Vagelis and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - KDD25
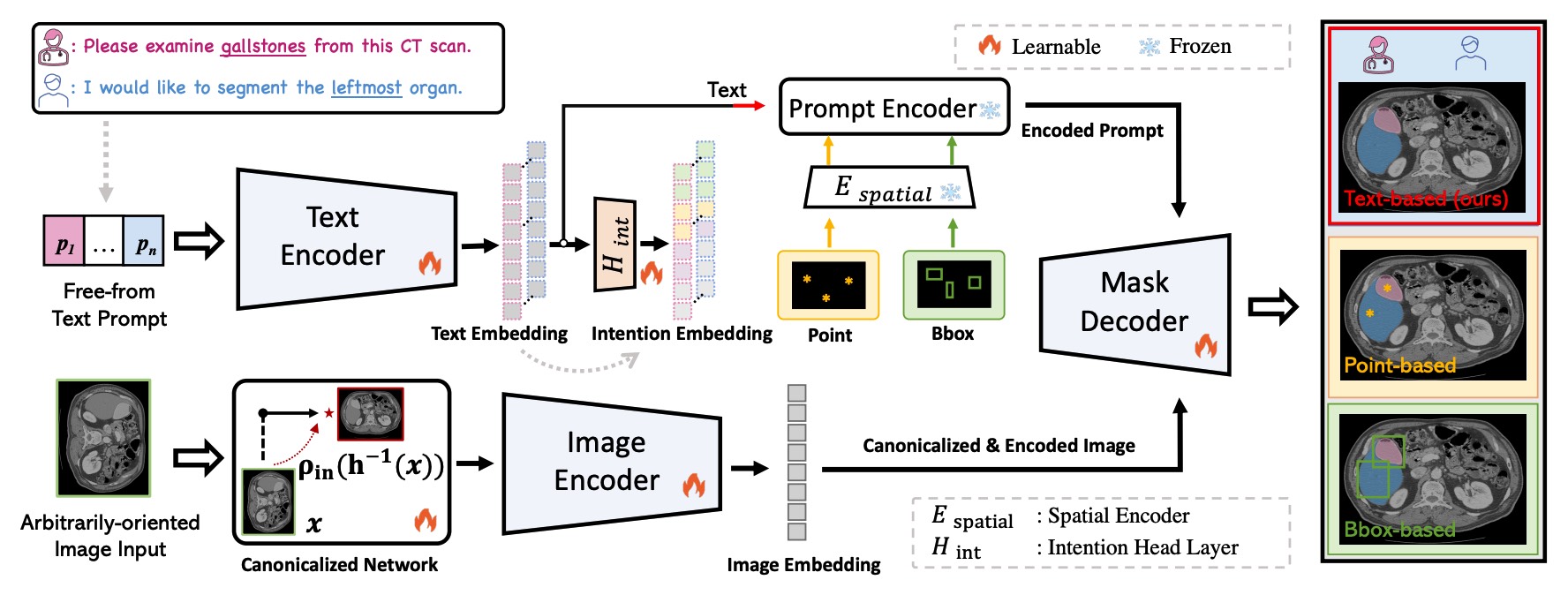 Segment as You Wish–Free-Form Language-Based Segmentation for Medical ImagesLongchao Da, Rui Wang, Xiaojian Xu , and 4 more authorsIn , 2025
Segment as You Wish–Free-Form Language-Based Segmentation for Medical ImagesLongchao Da, Rui Wang, Xiaojian Xu , and 4 more authorsIn , 2025Medical imaging is crucial for diagnosing a patient’s health condition, and accurate segmentation of these images is essential for isolating regions of interest to ensure precise diagnosis and treatment planning. Existing methods primarily rely on bounding boxes or point-based prompts, while few have explored text-related prompts, despite clinicians often describing their observations and instructions in natural language. To address this gap, we first propose a RAG-based free-form text prompt generator, that leverages the domain corpus to generate diverse and realistic descriptions. Then, we introduce FLanS, a novel medical image segmentation model that handles various free-form text prompts, including professional anatomy-informed queries, anatomy-agnostic position-driven queries, and anatomy-agnostic size-driven queries. Additionally, our model also incorporates a symmetry-aware canonicalization module to ensure consistent, accurate segmentations across varying scan orientations and reduce confusion between the anatomical position of an organ and its appearance in the scan. FLanS is trained on a large-scale dataset of over 100k medical images from 7 public datasets. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the model’s superior language understanding and segmentation precision, along with a deep comprehension of the relationship between them, outperforming SOTA baselines on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets.
@inproceedings{da2024prompt, title = {Segment as You Wish--Free-Form Language-Based Segmentation for Medical Images}, author = {Da, Longchao and Wang, Rui and Xu, Xiaojian and Bhatia, Parminder and Kass-Hout, Taha and Wei, Hua and Xiao, Cao}, year = {2025}, } - ICML25
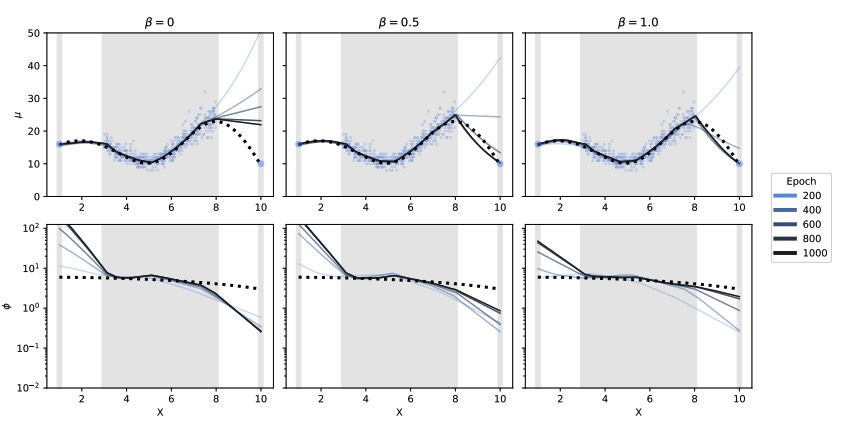 Flexible Heteroscedastic Count Regression with Deep Double Poisson NetworksSpencer Young, Porter Jenkins, Longchao Da , and 2 more authors2025
Flexible Heteroscedastic Count Regression with Deep Double Poisson NetworksSpencer Young, Porter Jenkins, Longchao Da , and 2 more authors2025Neural networks that can produce accurate, input-conditional uncertainty representations are critical for real-world applications. Recent progress on heteroscedastic continuous regression has shown great promise for calibrated uncertainty quantification on complex tasks, like image regression. However, when these methods are applied to discrete regression tasks, such as crowd counting, ratings prediction, or inventory estimation, they tend to produce predictive distributions with numerous pathologies. We propose to address these issues by training a neural network to output the parameters of a Double Poisson distribution, which we call the Deep Double Poisson Network (DDPN). In contrast to existing methods that are trained to minimize Gaussian negative log likelihood (NLL), DDPNs produce a proper probability mass function over discrete output. Additionally, DDPNs naturally model under-, over-, and equi-dispersion, unlike networks trained with the more rigid Poisson and Negative Binomial parameterizations. We show DDPNs 1) vastly outperform existing discrete models; 2) meet or exceed the accuracy and flexibility of networks trained with Gaussian NLL; 3) produce proper predictive distributions over discrete counts; and 4) exhibit superior out-of-distribution detection. DDPNs can easily be applied to a variety of count regression datasets including tabular, image, point cloud, and text data.
@article{young2024flexible, title = {Flexible Heteroscedastic Count Regression with Deep Double Poisson Networks}, author = {Young, Spencer and Jenkins, Porter and Da, Longchao and Dotson, Jeff and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - SDM25
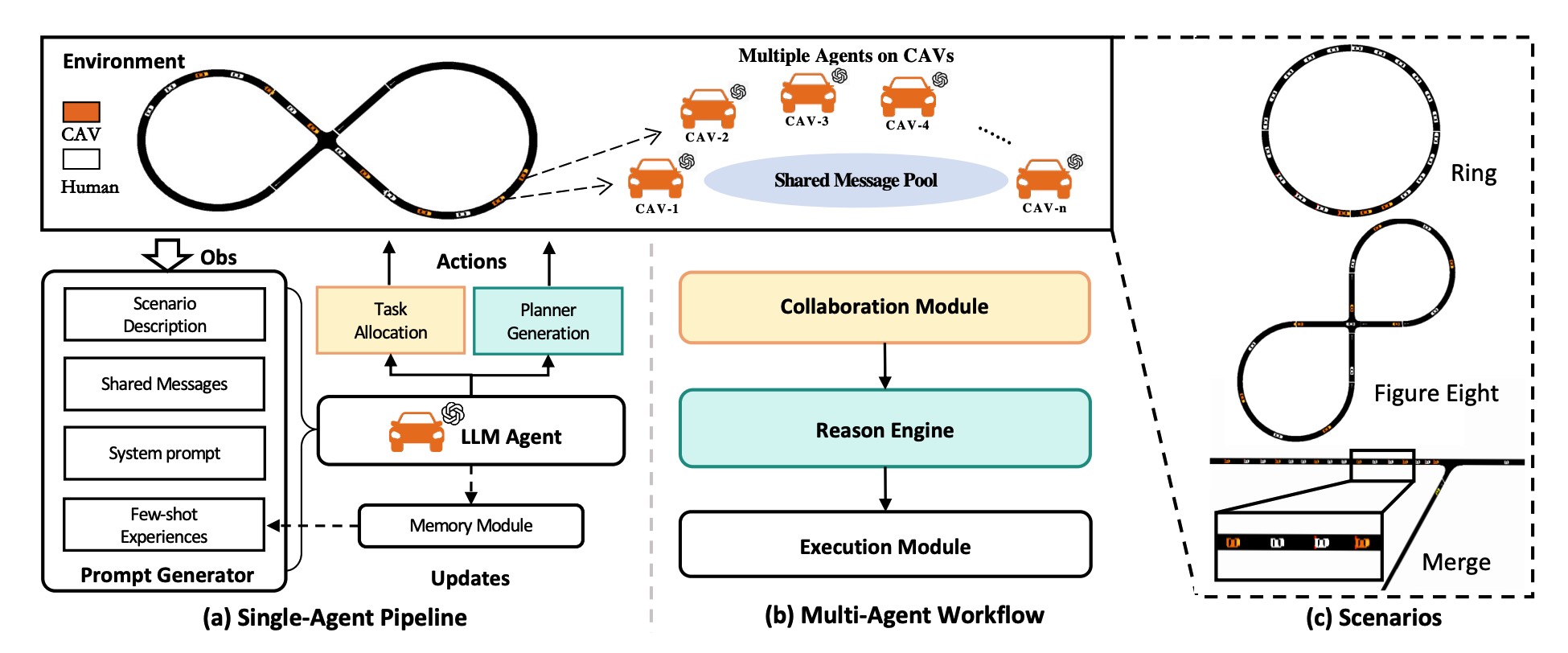 CoMAL: Collaborative Multi-Agent Large Language Models for Mixed-Autonomy TrafficLongchao Da, Huaiyuan* Yao, Vishnu Nandam , and 4 more authors2025
CoMAL: Collaborative Multi-Agent Large Language Models for Mixed-Autonomy TrafficLongchao Da, Huaiyuan* Yao, Vishnu Nandam , and 4 more authors2025The integration of autonomous vehicles into urban traffic has great potential to improve efficiency by reducing congestion and optimizing traffic flow systematically. In this paper, we introduce CoMAL (Collaborative Multi-Agent LLMs), a framework designed to address the mixed-autonomy traffic problem by collaboration among autonomous vehicles to optimize traffic flow. CoMAL is built upon large language models, operating in an interactive traffic simulation environment. It utilizes a Perception Module to observe surrounding agents and a Memory Module to store strategies for each agent. The overall workflow includes a Collaboration Module that encourages autonomous vehicles to discuss the effective strategy and allocate roles, a reasoning engine to determine optimal behaviors based on assigned roles, and an Execution Module that controls vehicle actions using a hybrid approach combining rule-based models. Experimental results demonstrate that CoMAL achieves superior performance on the Flow benchmark. Additionally, we evaluate the impact of different language models and compare our framework with reinforcement learning approaches. It highlights the strong cooperative capability of LLM agents and presents a promising solution to the mixed-autonomy traffic challenge
@article{yao2024comal, title = {CoMAL: Collaborative Multi-Agent Large Language Models for Mixed-Autonomy Traffic}, author = {Da, Longchao and Yao, Huaiyuan and Nandam, Vishnu and Turnau, Justin and Liu, Zhiwei and Pang, Linsey and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, } - SDM25
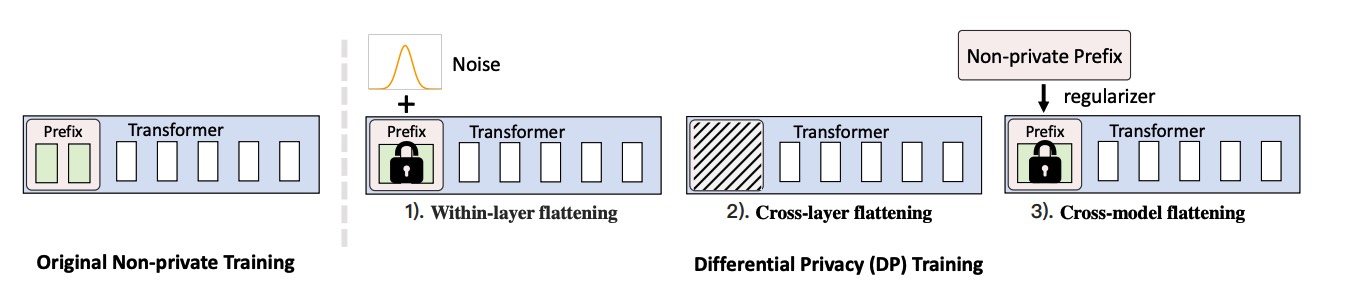 Privacy-preserving Fine-tuning of Large Language Models through FlatnessTiejin Chen, Longchao Da, Huixue Zhou , and 4 more authors2025
Privacy-preserving Fine-tuning of Large Language Models through FlatnessTiejin Chen, Longchao Da, Huixue Zhou , and 4 more authors2025The privacy concerns associated with the use of Large Language Models (LLMs) have grown recently with the development of LLMs such as ChatGPT. Differential Privacy (DP) techniques are explored in existing work to mitigate their privacy risks at the cost of generalization degradation. Our paper reveals that the flatness of DP-trained models’ loss landscape plays an essential role in the trade-off between their privacy and generalization. We further propose a holistic framework to enforce appropriate weight flatness, which substantially improves model generalization with competitive privacy preservation. It innovates from three coarse-to-grained levels, including perturbation-aware min-max optimization on model weights within a layer, flatness-guided sparse prefix-tuning on weights across layers, and weight knowledge distillation between DP & non-DP weights copies. Comprehensive experiments of both black-box and white-box scenarios are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposal in enhancing generalization and maintaining DP characteristics. For instance, on text classification dataset QNLI, DP-Flat achieves similar performance with non-private full fine-tuning but with DP guarantee under privacy budget, and even better performance given higher privacy budgets. Codes are provided in the supplement.
@article{chen2024privacy, title = {Privacy-preserving Fine-tuning of Large Language Models through Flatness}, author = {Chen, Tiejin and Da, Longchao and Zhou, Huixue and Li, Pingzhi and Zhou, Kaixiong and Chen, Tianlong and Wei, Hua}, year = {2025}, }
2024
- pre-print
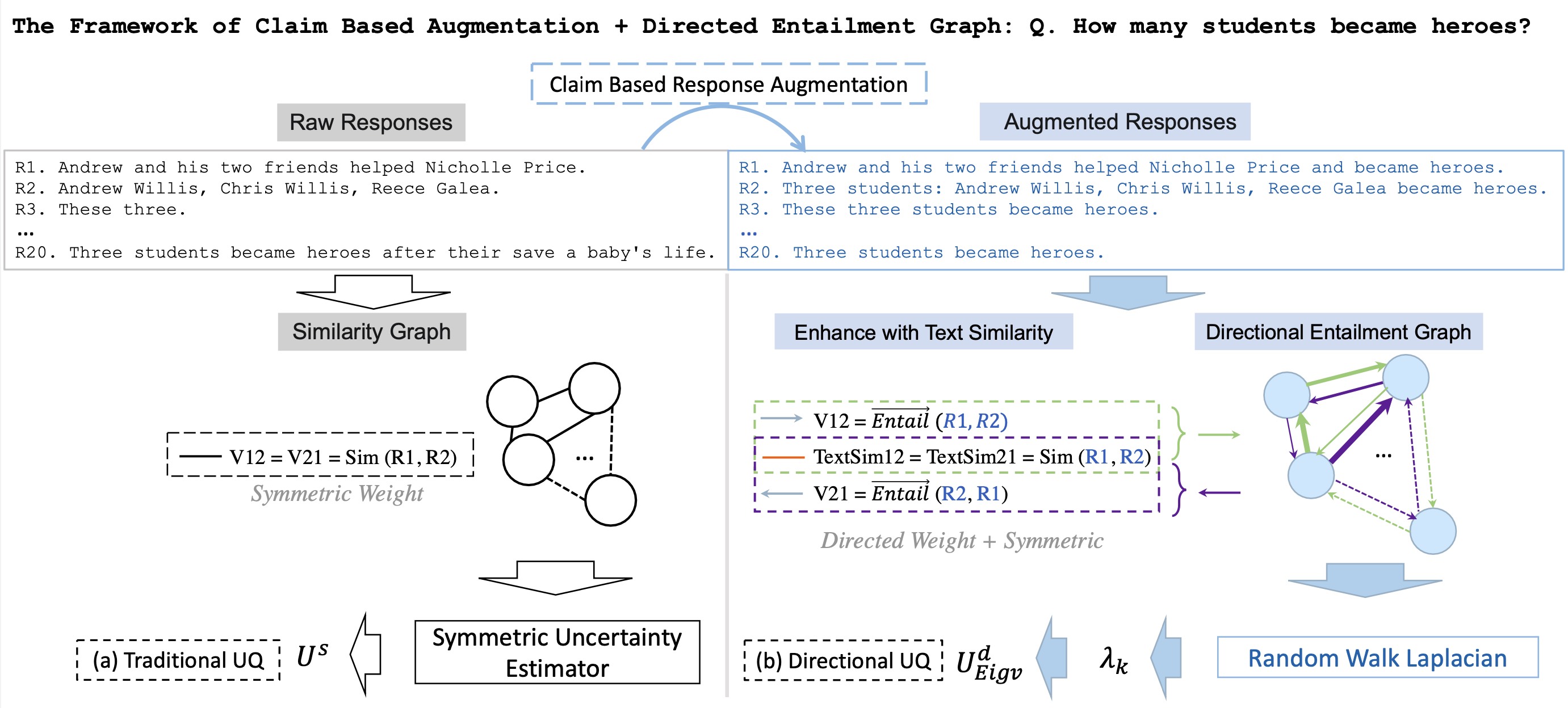 LLM Uncertainty Quantification through Directional Entailment Graph and Claim Level Response AugmentationLongchao Da, Tiejin Chen, Lu Cheng , and 1 more author2024
LLM Uncertainty Quantification through Directional Entailment Graph and Claim Level Response AugmentationLongchao Da, Tiejin Chen, Lu Cheng , and 1 more author2024The Large language models (LLMs) have showcased superior capabilities in sophisticated tasks across various domains, stemming from basic question-answer (QA), they are nowadays used as decision assistants or explainers for unfamiliar content. However, they are not always correct due to the data sparsity in specific domain corpus, or the model’s hallucination problems. Given this, how much should we trust the responses from LLMs? This paper studies the question in two aspects, first, we find measuring directly on raw responses from LLMs is easy to be vague due to the lack of context, second this paper identifies the oversight in existing work regarding the neglect of directional relationships between sentences. To tackle the challenges, we first provide a claim-based response augmentation, by completing the fine-grained claims in raw response, and augmenting into a more explicit description, it removes the randomness, improves the completeness, and provides a response set that robustly represents the knowledge of LLMs. Then, second, methodologically we present a way to evaluate the uncertainty that captures the directional instability between sentences by constructing a directional graph using entailment probabilities, and conducting Random Walk Laplacian given the asymmetric property in the directed graph, then the uncertainty is aggregated by the derived eigenvalues from the Laplacian process. We conducted extensive experiments and empirically demonstrated the superiority of our proposed solutions.
@article{da2024llm, title = {LLM Uncertainty Quantification through Directional Entailment Graph and Claim Level Response Augmentation}, author = {Da, Longchao and Chen, Tiejin and Cheng, Lu and Wei, Hua}, year = {2024}, } - CIKM24
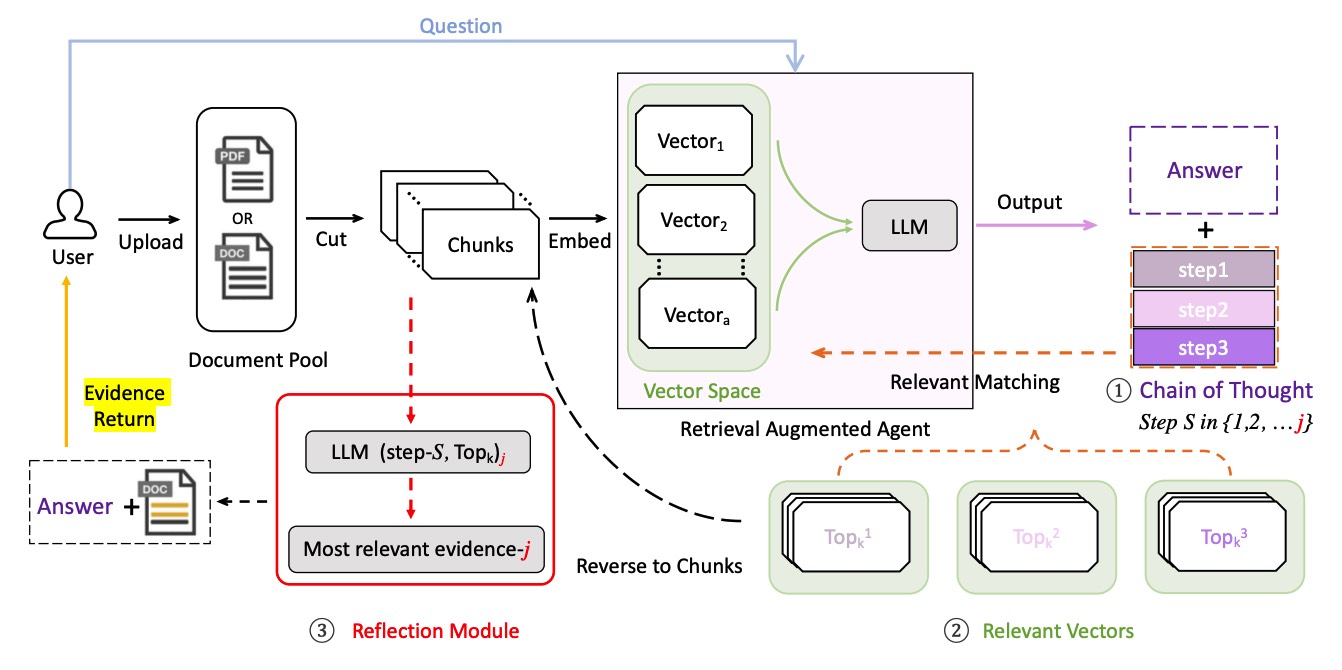 EvidenceChat: A RAG Enhanced LLM Framework for Trustworthy and Evidential Response GenerationLongchao Da, Parth Mitesh Shah, Ananya Singh , and 1 more author2024
EvidenceChat: A RAG Enhanced LLM Framework for Trustworthy and Evidential Response GenerationLongchao Da, Parth Mitesh Shah, Ananya Singh , and 1 more author2024The Large Language Model has become an important assistant for many of human’s decision-making. However, a side note almost comes along with every single LLM:‘LLMs can make mistakes. Be careful with important info’. This reveals the fact that not all of the information from LLMs is trustworthy, and people still need to judge by themselves. Yet, the hallucination is so powerful that a made-up conclusion could even come with a seemingly plausible reason, which brings intricate challenges and a trust crisis among users. This paper proposes EvidenceChat, a framework that tackles this issue in a retrieval-augmented fashion, specifically, when the user uploads a material document, an indexed vector space will be constructed based on text embeddings, which helps construct a retrieval-augmented agent, enhancing the agent’s responses with additional knowledge beyond its training corpus. Then, we propose a three-step evidential retrieval method to accurately locate the evidence of a language agent’s conclusion in the source context: Chain-of-Thought (CoT) logic generation, top-k relevant chunk vector matching, and a self-reflection-based precise sentence identification. We demonstrate that our method improves the existing models’ performance in terms of identifying the exact evidence in a free-form context, providing a reliable way to examine the resources of LLM’s conclusion and help with the judgment of the trustworthiness. The dataset and code will be released.
@article{da2024evidencechat, title = {EvidenceChat: A RAG Enhanced LLM Framework for Trustworthy and Evidential Response Generation}, author = {Da, Longchao and Shah, Parth Mitesh and Singh, Ananya and Wei, Hua}, year = {2024}, } - NeurIPS24
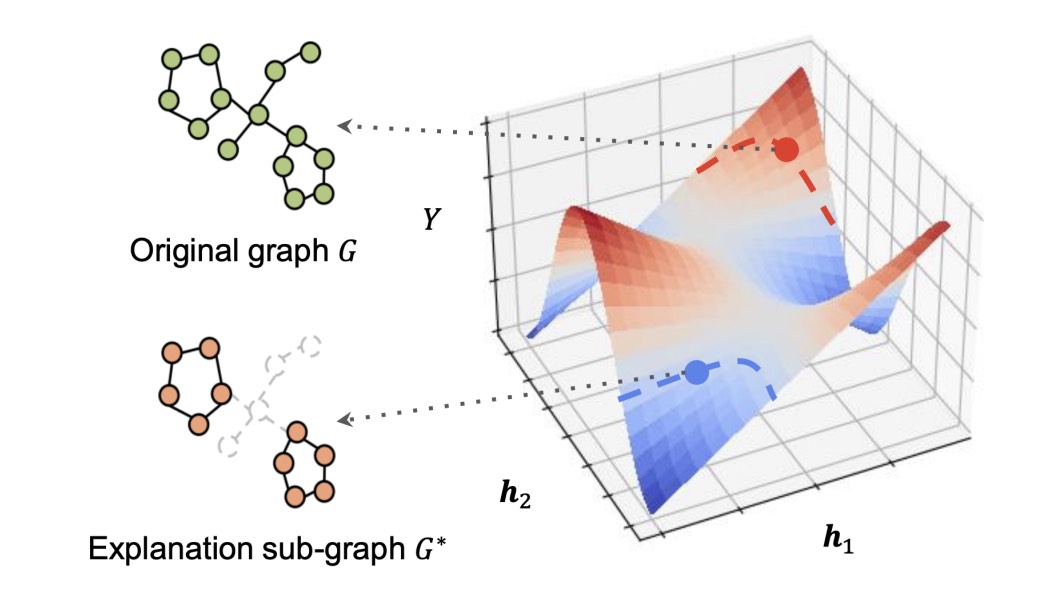 RegExplainer: Generating Explanations for Graph Neural Networks in Regression TasksJiaxing Zhang, Zhuomin Chen, Hao Mei , and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 2024 Neural Information Processing Systems , 2024
RegExplainer: Generating Explanations for Graph Neural Networks in Regression TasksJiaxing Zhang, Zhuomin Chen, Hao Mei , and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the 2024 Neural Information Processing Systems , 2024Graph regression is a fundamental task and has received increasing attention in a wide range of graph learning tasks. However, the inference process is often not interpretable. Most existing explanation techniques are limited to understanding GNN behaviors in classification tasks. In this work, we seek an explanation to interpret the graph regression models (XAIG-R). We show that existing methods overlook the distribution shifting and continuously ordered decision boundary, which hinders them away from being applied in the regression tasks. To address these challenges, we propose a novel objective based on the information bottleneck theory and introduce a new mix-up framework, which could support various GNNs in a model-agnostic manner. We further present a contrastive learning strategy to tackle the continuously ordered labels in regression task. To empirically verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, we introduce three benchmark datasets and a real-life dataset for evaluation. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness of the proposed method in interpreting GNN models in regression tasks.
@inproceedings{da2024prompu, title = {RegExplainer: Generating Explanations for Graph Neural Networks in Regression Tasks}, author = {Zhang, Jiaxing and Chen, Zhuomin and Mei, Hao and Da, Longchao and Luo, Dongsheng and Wei, Hua}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2024 Neural Information Processing Systems}, year = {2024}, } - AAAI24
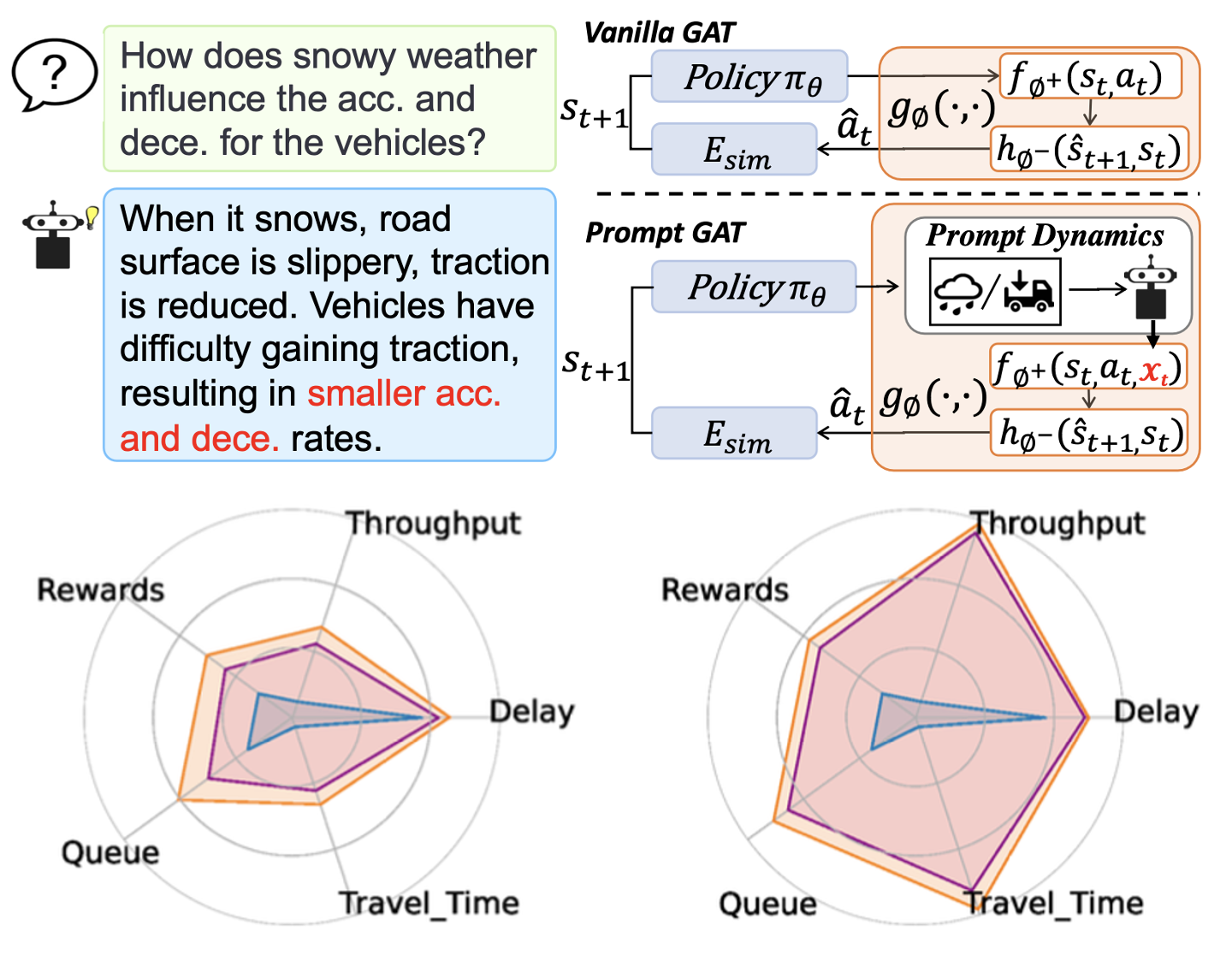 Prompt to Transfer: Sim-to-Real Transfer for Traffic Signal Control with Prompt LearningLongchao Da, Minquan Gao, Hao Mei , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence , 2024
Prompt to Transfer: Sim-to-Real Transfer for Traffic Signal Control with Prompt LearningLongchao Da, Minquan Gao, Hao Mei , and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence , 2024Numerous solutions are proposed for the Traffic Signal Con- trol (TSC) tasks aiming to provide efficient transportation and alleviate traffic congestion. Recently, promising results have been attained by Reinforcement Learning (RL) methods through trial and error in simulators, bringing confidence in solving cities’ congestion problems. However, performance gaps still exist when simulator-trained policies are deployed to the real world. This issue is mainly introduced by the sys- tem dynamic difference between the training simulators and the real-world environments. In this work, we leverage the knowledge of Large Language Models (LLMs) to understand and profile the system dynamics by a prompt-based grounded action transformation to bridge the performance gap. Specifi- cally, this paper exploits the pre-trained LLM’s inference abil- ity to understand how traffic dynamics change with weather conditions, traffic states, and road types. Being aware of the changes, the policies’ action is taken and grounded based on realistic dynamics, thus helping the agent learn a more realistic policy. We conduct experiments on four different scenarios to show the effectiveness of the proposed PromptGAT’s ability to mitigate the performance gap of reinforcement learning from simulation to reality (sim-to-real).
@inproceedings{da2024prompv, title = {Prompt to Transfer: Sim-to-Real Transfer for Traffic Signal Control with Prompt Learning}, author = {Da, Longchao and Gao, Minquan and Mei, Hao and Wei, Hua}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1609/aaai.v38i1.27758}, } - AAAI24
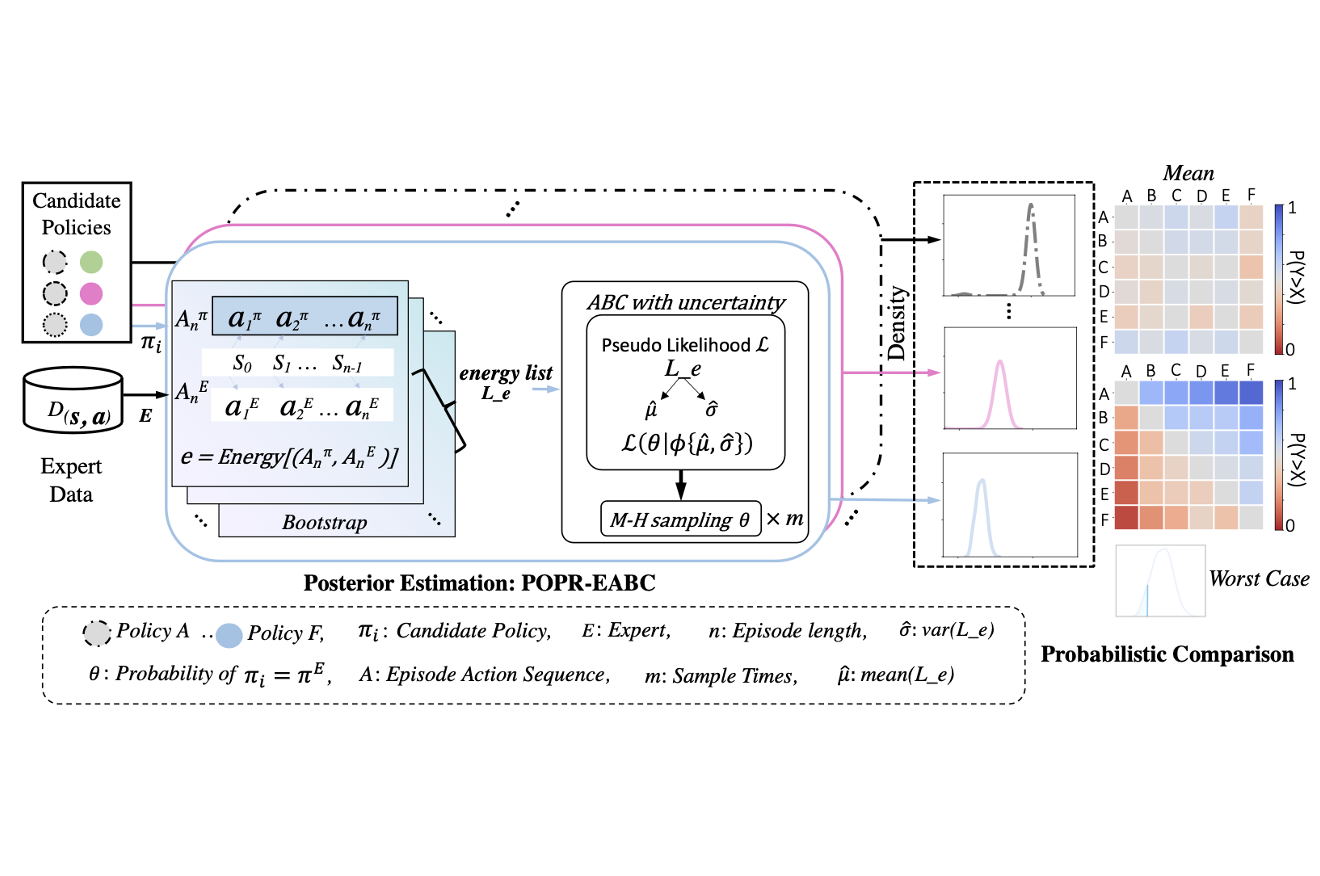 Probabilistic Offline Policy Ranking with Approximate Bayesian ComputationLongchao Da, Porter Jenkins, Trevor Schwantes , and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence , 2024
Probabilistic Offline Policy Ranking with Approximate Bayesian ComputationLongchao Da, Porter Jenkins, Trevor Schwantes , and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence , 2024In practice, it is essential to compare and rank candidate policies offline before real-world deployment for safety and reliability. Prior work seeks to solve this offline policy ranking (OPR) problem through value-based methods, such as Off-policy evaluation (OPE). However, they fail to analyze special case performance (e.g., worst or best cases), due to the lack of holistic characterization of policies’ performance. It is even more difficult to estimate precise policy values when the reward is not fully accessible under sparse settings. In this paper, we present Probabilistic Offline Policy Ranking (POPR), a framework to address OPR problems by leveraging expert data to characterize the probability of a candidate policy behaving like experts, and approximating its entire performance posterior distribution to help with ranking. POPR does not rely on value estimation, and the derived performance posterior can be used to distinguish candidates in worst-, best-, and average-cases. To estimate the posterior, we propose POPR-EABC, an Energy-based Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) method conducting likelihood-free inference. POPR-EABC reduces the heuristic nature of ABC by a smooth energy function, and improves the sampling efficiency by a pseudo-likelihood. We empirically demonstrate that POPR-EABC is adequate for evaluating policies in both discrete and continuous action spaces across various experiment environments, and facilitates probabilistic comparisons of candidate policies before deployment.
@inproceedings{da2024probabilistic, title = {Probabilistic Offline Policy Ranking with Approximate Bayesian Computation}, author = {Da, Longchao and Jenkins, Porter and Schwantes, Trevor and Dotson, Jeffrey and Wei, Hua}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence}, volume = {38}, number = {18}, pages = {20370--20378}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1609/aaai.v38i18.30019}, } - IJMLC
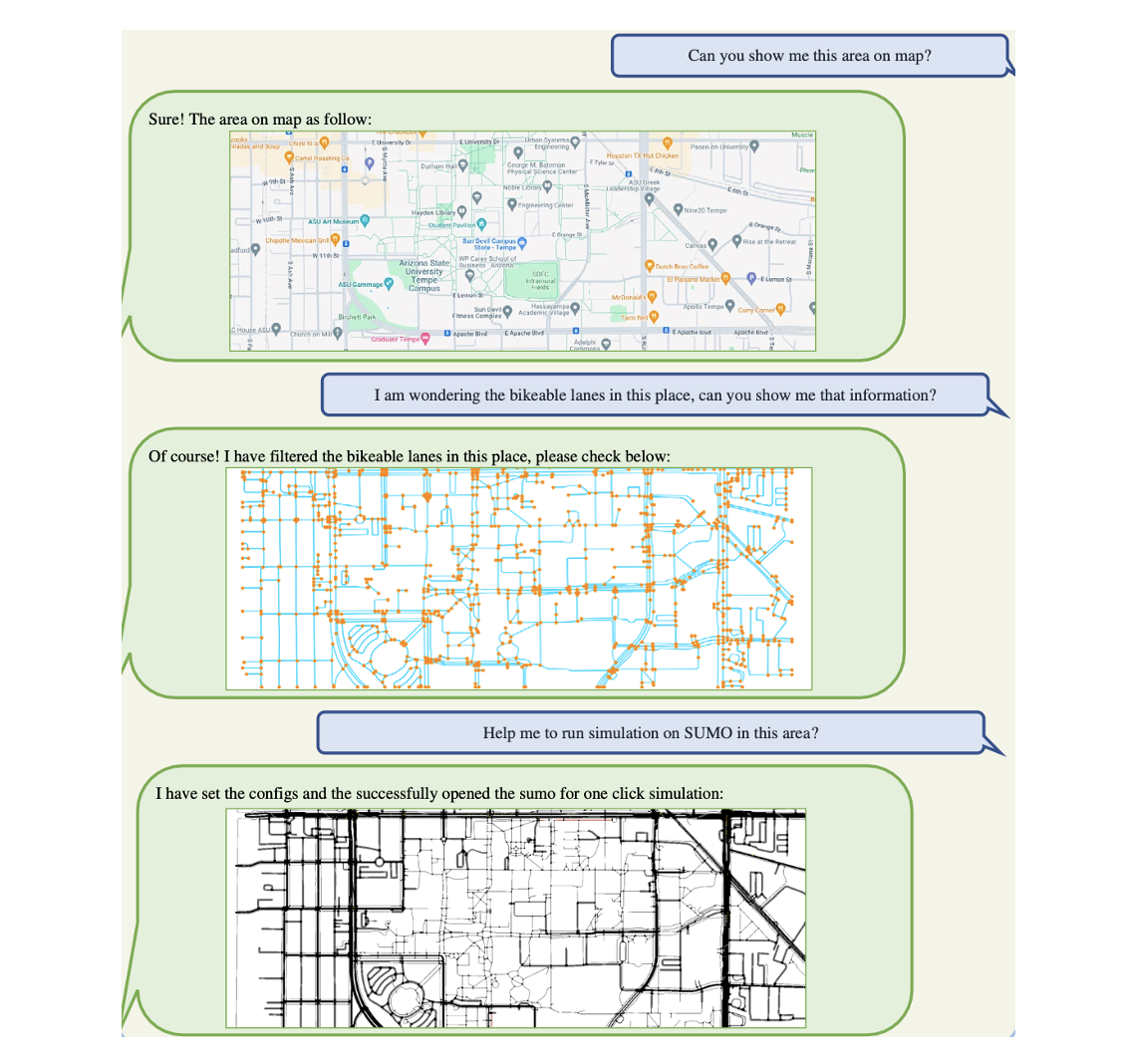 Open-ti: Open traffic intelligence with augmented language modelLongchao Da, Kuanru Liou, Tiejin Chen , and 4 more authorsInternational Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2024
Open-ti: Open traffic intelligence with augmented language modelLongchao Da, Kuanru Liou, Tiejin Chen , and 4 more authorsInternational Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2024Transportation has greatly benefited the cities’ development in the modern civilization process. Intelligent transportation, leveraging advanced computer algorithms, could further increase people’s daily commuting efficiency. However, intelligent transportation, as a cross-discipline, often requires practitioners to comprehend complicated algorithms and obscure neural networks, bringing a challenge for the advanced techniques to be trusted and deployed in practical industries. Recognizing the expressiveness of the pre-trained large language models, especially the potential of being augmented with abilities to understand and execute intricate commands, we introduce Open-TI. Serving as a bridge to mitigate the industry-academic gap, Open-TI is an innovative model targeting the goal of Turing Indistinguishable Traffic Intelligence, it is augmented with the capability to harness external traffic analysis packages based on existing conversations. Marking its distinction, Open-TI is the first method capable of conducting exhaustive traffic analysis from scratch—spanning from map data acquisition to the eventual execution in complex simulations. Besides, Open-TI is able to conduct task-specific embodiment like training and adapting the traffic signal control policies (TSC), explore demand optimizations, etc. Furthermore, we explored the viability of LLMs directly serving as control agents, by understanding the expected intentions from Open-TI, we designed an agent-to-agent communication mode to support Open-TI conveying messages to ChatZero (control agent), and then the control agent would choose from the action space to proceed the execution. We eventually provide the formal implementation structure, and the open-ended design invites further community-driven enhancements. A demo video is provided at: https://youtu.be/pZ4-5PXz9Xs.
@article{da2024open, title = {Open-ti: Open traffic intelligence with augmented language model}, author = {Da, Longchao and Liou, Kuanru and Chen, Tiejin and Zhou, Xuesong and Luo, Xiangyong and Yang, Yezhou and Wei, Hua}, journal = {International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics}, pages = {1--26}, year = {2024}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s13042-024-02190-8}, } - ECML-PKDD24
 CityFlowER: An Efficient and Realistic Traffic Simulator with Embedded Machine Learning ModelsLongchao Da, Chen Chu, Weinan Zhang , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2402.06127, 2024
CityFlowER: An Efficient and Realistic Traffic Simulator with Embedded Machine Learning ModelsLongchao Da, Chen Chu, Weinan Zhang , and 1 more authorarXiv preprint arXiv:2402.06127, 2024Traffic simulation is an essential tool for transportation infrastructure planning, intelligent traffic control policy learning, and traffic flow analysis. Its effectiveness relies heavily on the realism of the simulators used. Traditional traffic simulators, such as SUMO and CityFlow, are often limited by their reliance on rule-based models with hyperparameters that oversimplify driving behaviors, resulting in unrealistic simulations. To enhance realism, some simulators have provided Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to interact with Machine Learning (ML) models, which learn from observed data and offer more sophisticated driving behavior models. However, this approach faces challenges in scalability and time efficiency as vehicle numbers increase. Addressing these limitations, we introduce CityFlowER, an advancement over the existing CityFlow simulator, designed for efficient and realistic city-wide traffic simulation. CityFlowER innovatively pre-embeds ML models within the simulator, eliminating the need for external API interactions and enabling faster data computation. This approach allows for a blend of rule-based and ML behavior models for individual vehicles, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency, particularly in large-scale simulations. We provide detailed comparisons with existing simulators, implementation insights, and comprehensive experiments to demonstrate CityFlowER’s superiority in terms of realism, efficiency, and adaptability.
@article{da2024cityflower, title = {CityFlowER: An Efficient and Realistic Traffic Simulator with Embedded Machine Learning Models}, author = {Da, Longchao and Chu, Chen and Zhang, Weinan and Wei, Hua}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.06127}, year = {2024}, } - CIKM24
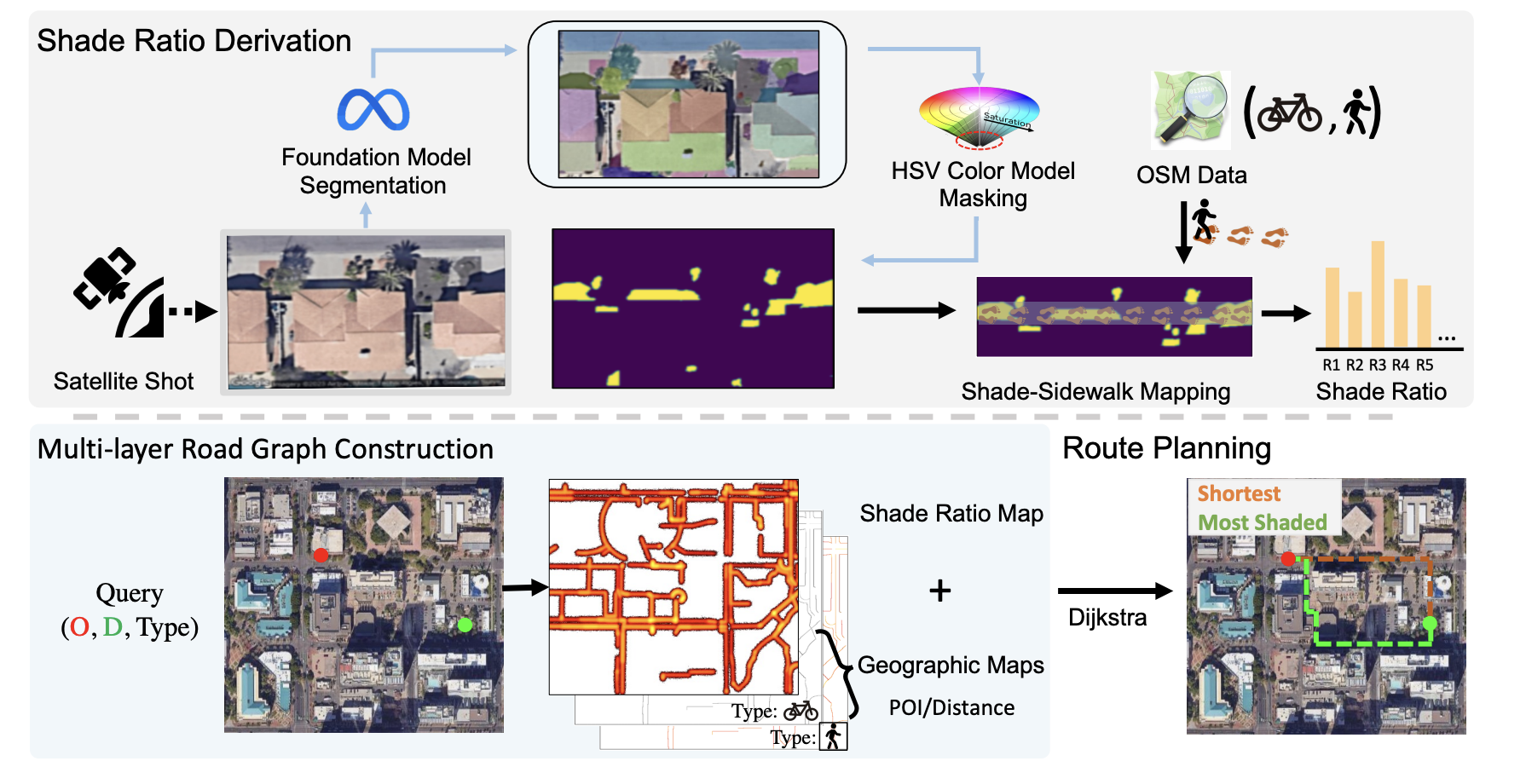 Shaded Route Planning Using Active Segmentation and Identification of Satellite ImagesLongchao Da, Rohan Chhibba, Rushabh Jaiswal , and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2407.13689, 2024
Shaded Route Planning Using Active Segmentation and Identification of Satellite ImagesLongchao Da, Rohan Chhibba, Rushabh Jaiswal , and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2407.13689, 2024Heatwaves pose significant health risks, particularly due to prolonged exposure to high summer temperatures. Vulnerable groups, especially pedestrians and cyclists on sun-exposed sidewalks, motivate the development of a route planning method that incorporates somatosensory temperature effects through shade ratio consideration. This paper is the first to introduce a pipeline that utilizes segmentation foundation models to extract shaded areas from high-resolution satellite images. These areas are then integrated into a multi-layered road map, enabling users to customize routes based on a balance between distance and shade exposure, thereby enhancing comfort and health during outdoor activities. Specifically, we construct a graph-based representation of the road map, where links indicate connectivity and are updated with shade ratio data for dynamic route planning. This system is already implemented online, with a video demonstration, and will be specifically adapted to assist travelers during the 2024 Olympic Games in Paris.
@article{da2024shaded, title = {Shaded Route Planning Using Active Segmentation and Identification of Satellite Images}, author = {Da, Longchao and Chhibba, Rohan and Jaiswal, Rushabh and Middel, Ariane and Wei, Hua}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.13689}, year = {2024}, tutorial = {http://18.191.152.144:9999/tutorial.html}, } - ITSC24
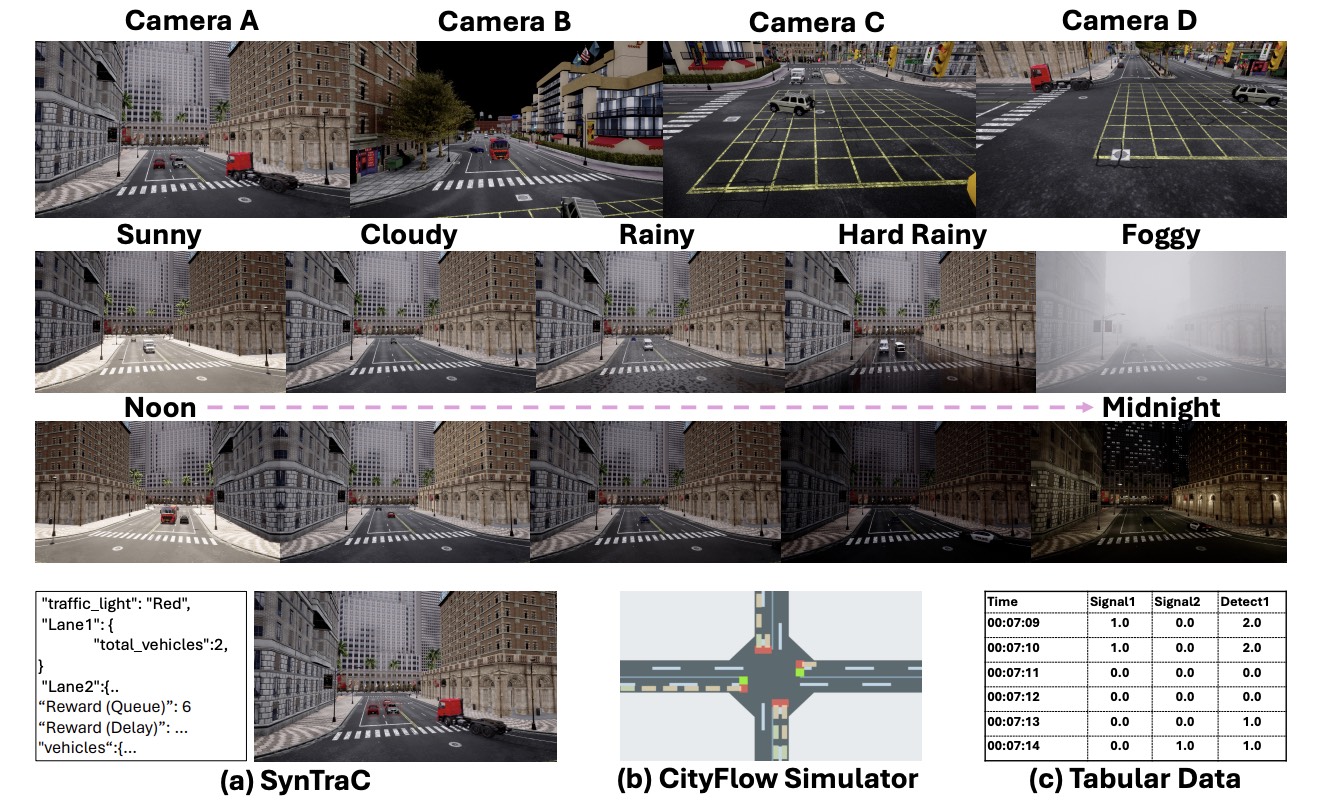 SynTraC: A Synthetic Dataset for Traffic Signal Control from Traffic Monitoring CamerasTiejin Chen, Prithvi Shirke, Bharatesh Chakravarthi , and 5 more authors2024
SynTraC: A Synthetic Dataset for Traffic Signal Control from Traffic Monitoring CamerasTiejin Chen, Prithvi Shirke, Bharatesh Chakravarthi , and 5 more authors2024This paper introduces SynTraC, the first public image-based traffic signal control dataset, aimed at bridging the gap between simulated environments and real-world traffic management challenges. Unlike traditional datasets for traffic signal control which aim to provide simplified feature vectors like vehicle counts from traffic simulators, SynTraC provides real-style images from the CARLA simulator with annotated features, along with traffic signal states. This image-based dataset comes with diverse real-world scenarios, including varying weather and times of day. Additionally, SynTraC also provides different reward values for advanced traffic signal control algorithms like reinforcement learning. Experiments with SynTraC demonstrate that it is still an open challenge to image-based traffic signal control methods compared with feature-based control methods, indicating our dataset can further guide the development of future algorithms.
@misc{chen2024syntracsyntheticdatasettraffic, title = {SynTraC: A Synthetic Dataset for Traffic Signal Control from Traffic Monitoring Cameras}, author = {Chen, Tiejin and Shirke, Prithvi and Chakravarthi, Bharatesh and Vaghela, Arpitsinh and Da, Longchao and Lu, Duo and Yang, Yezhou and Wei, Hua}, year = {2024}, eprint = {2408.09588}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.09588} }
2023
- CASE23
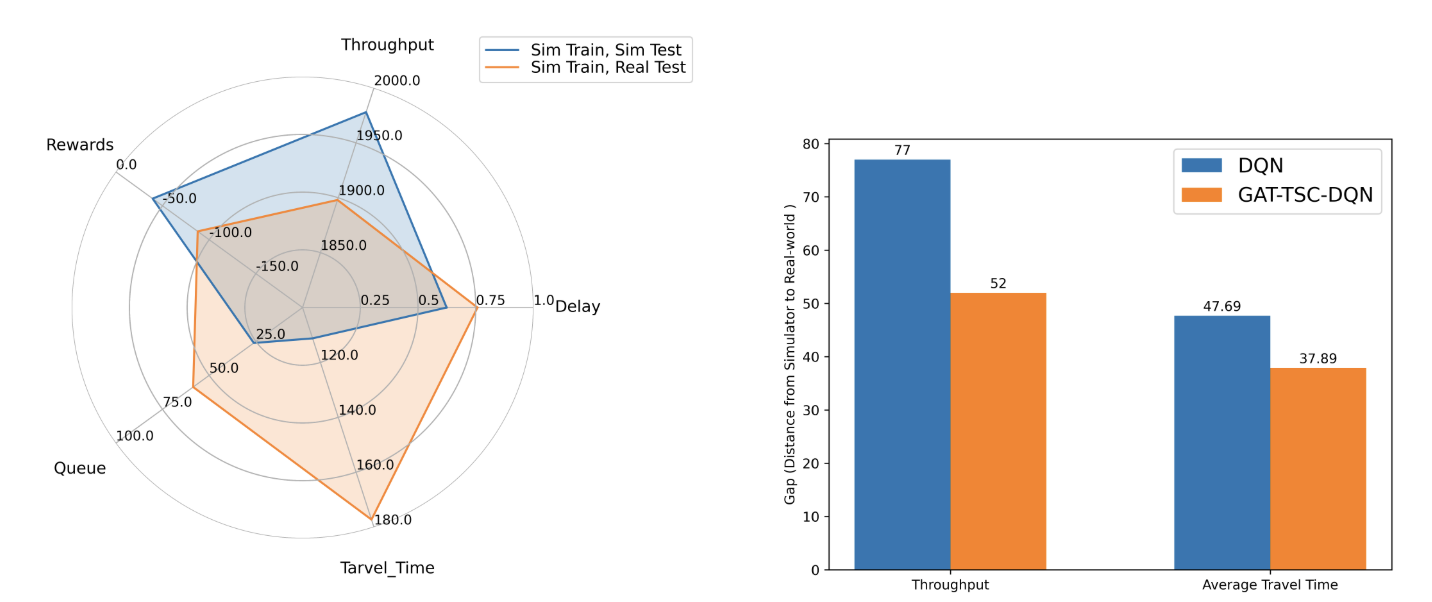 Sim2Real Transfer for Traffic Signal ControlLongchao Da, Hao Mei, Romir Sharma , and 1 more authorIn IEEE 19th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering , 2023
Sim2Real Transfer for Traffic Signal ControlLongchao Da, Hao Mei, Romir Sharma , and 1 more authorIn IEEE 19th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering , 2023Traffic signal control is a complex and important task that affects the daily lives of millions of people. Reinforcement Learning (RL) has shown promising results in optimizing traffic signal control, but transferring learned policies from simulation to the real world remains a challenge due to the domain gap between the simulation and the complex real-life scenario. In this paper, we utilize grounded action transformation to mitigate the domain shifting problem and improve Sim2Real transfer for RL-based traffic signal control. Grounded action transformation leverages the dynamics between the simulation and real-world actions to generate effective real-world actions. We evaluate our method on a simulated traffic environment and show that it significantly improves the performance of the transferred RL policy in the real world. Our results demonstrate the potential of grounded action transformation as a promising technique for Sim2Real transfer in RL-based traffic signal control.
@inproceedings{da2023sim2real, title = {Sim2Real Transfer for Traffic Signal Control}, author = {Da, Longchao and Mei, Hao and Sharma, Romir and Wei, Hua}, booktitle = {IEEE 19th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering}, pages = {1--2}, year = {2023}, organization = {IEEE}, } - Machine Learning
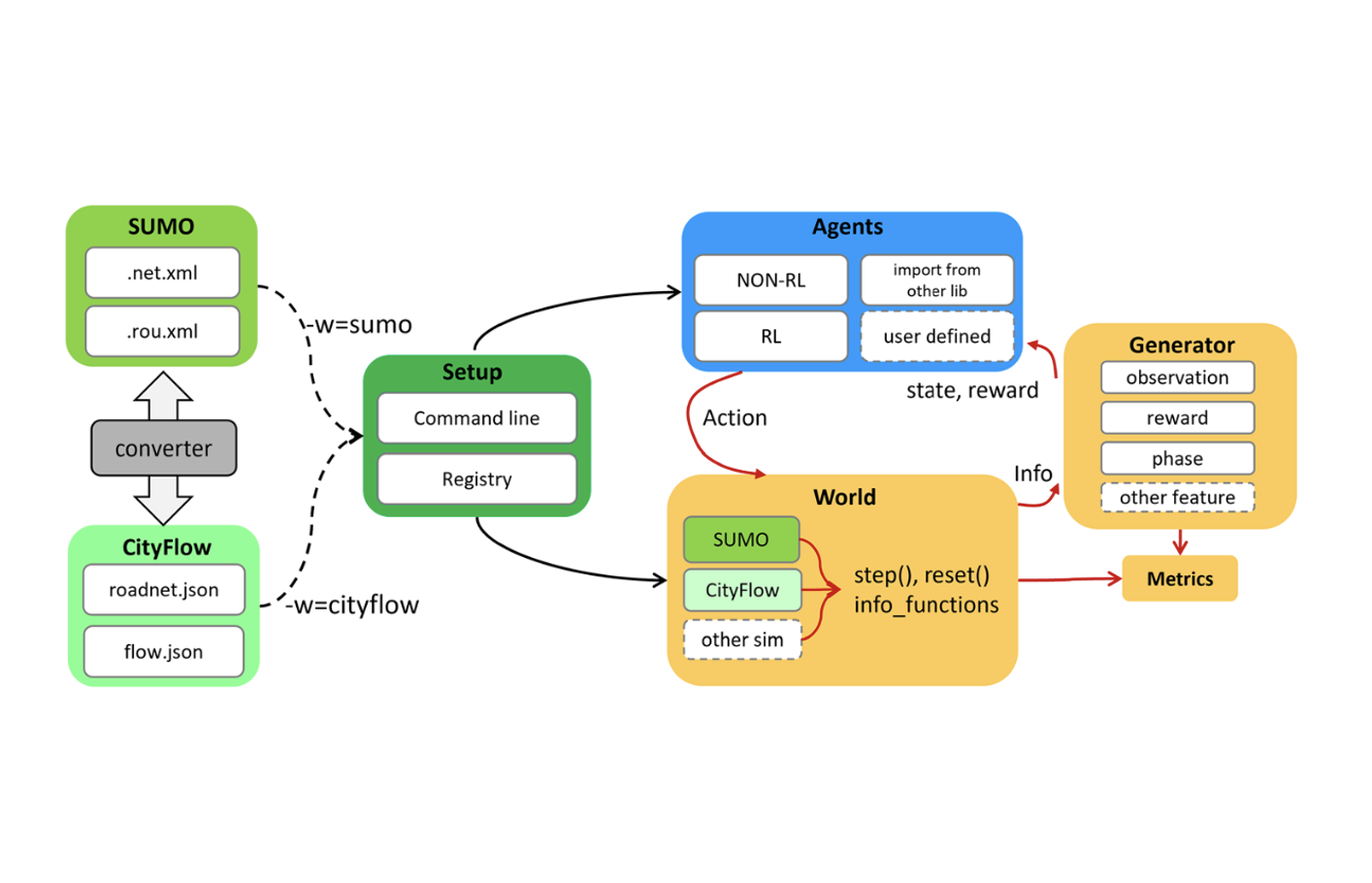 Libsignal: an open library for traffic signal controlHao Mei, Xiaoliang Lei, Longchao Da , and 2 more authorsMachine Learning, 2023
Libsignal: an open library for traffic signal controlHao Mei, Xiaoliang Lei, Longchao Da , and 2 more authorsMachine Learning, 2023This paper introduces a library for cross-simulator comparison of reinforcement learning models in traffic signal control tasks. This library is developed to implement recent state-of-the-art reinforcement learning models with extensible interfaces and unified cross-simulator evaluation metrics. It supports commonly-used simulators in traffic signal control tasks, including Simulation of Urban MObility(SUMO) and CityFlow, and multiple benchmark datasets for fair comparisons. We conducted experiments to validate our implementation of the models and to calibrate the simulators so that the experiments from one simulator could be referential to the other. Based on the validated models and calibrated environments, this paper compares and reports the performance of current state-of-the-art RL algorithms across different datasets and simulators. This is the first time that these methods have been compared fairly under the same datasets with different simulators.
@article{mei2023libsignal, title = {Libsignal: an open library for traffic signal control}, author = {Mei, Hao and Lei, Xiaoliang and Da, Longchao and Shi, Bin and Wei, Hua}, journal = {Machine Learning}, pages = {1--37}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Springer}, } - CDC23
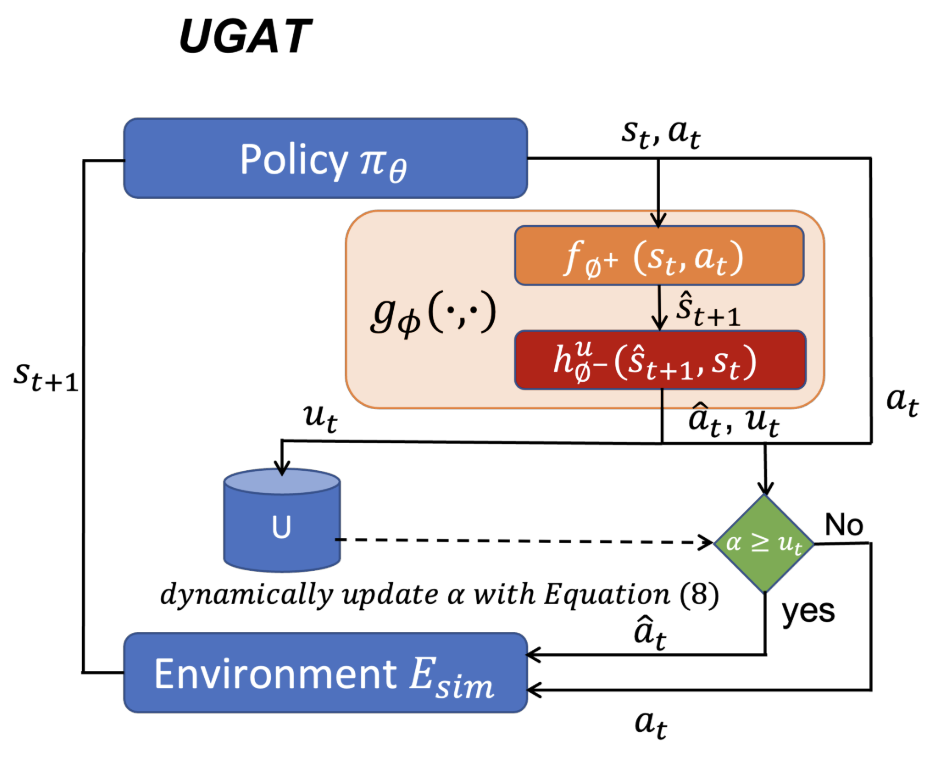 Uncertainty-aware Grounded Action Transformation towards Sim-to-Real Transfer for Traffic Signal ControlLongchao Da, Hao Mei, Romir Sharma , and 1 more authorIn 2023 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) , 2023
Uncertainty-aware Grounded Action Transformation towards Sim-to-Real Transfer for Traffic Signal ControlLongchao Da, Hao Mei, Romir Sharma , and 1 more authorIn 2023 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) , 2023Traffic signal control (TSC) is a complex and important task that affects the daily lives of millions of people. Reinforcement Learning (RL) has shown promising results in optimizing traffic signal control, but current RL-based TSC methods are mainly trained in simulation and suffer from the performance gap between simulation and the real world. In this paper, we propose a simulation-to-real-world (sim-to-real) transfer approach called UGAT, which transfers a learned policy trained from a simulated environment to a real-world environment by dynamically transforming actions in the simulation with uncertainty to mitigate the domain gap of transition dynamics. We evaluate our method on a simulated traffic environment and show that it significantly improves the performance of the transferred RL policy in the real world.
@inproceedings{da2023uncertainty, title = {Uncertainty-aware Grounded Action Transformation towards Sim-to-Real Transfer for Traffic Signal Control}, author = {Da, Longchao and Mei, Hao and Sharma, Romir and Wei, Hua}, booktitle = {2023 62nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC)}, pages = {1124--1129}, year = {2023}, organization = {IEEE}, }
2022
- ERA
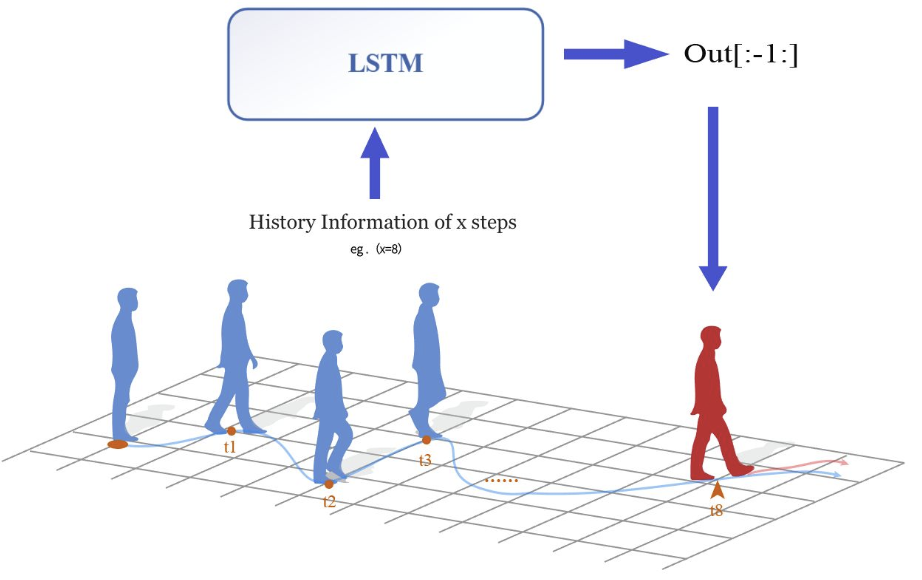 CrowdGAIL: A spatiotemporal aware method for agent navigationLongchao Da, and Hua WeiElectronic Research Archive, 2022
CrowdGAIL: A spatiotemporal aware method for agent navigationLongchao Da, and Hua WeiElectronic Research Archive, 2022Agent navigation has been a crucial task in today’s service and automated factories. Many efforts are to set specific rules for agents in a certain scenario to regulate the agent’s behaviors. However, not all situations could be in advance considered, which might lead to terrible performance in a real-world application. In this paper, we propose CrowdGAIL, a method to learn from expert behaviors as an instructing policy, can train most ’human-like’ agents in navigation problems without manually setting any reward function or beforehand regulations. First, the proposed model structure is based on generative adversarial imitation learning (GAIL), which imitates how humans take actions and move toward the target to a maximum extent, and by comparison, we prove the advantage of proximal policy optimization (PPO) to trust region policy optimization, thus, GAIL-PPO is what we base. Second, we design a special Sequential DemoBuffer compatible with the inner long short-term memory structure to apply spatiotemporal instruction on the agent’s next step. Third, the paper demonstrates the potential of the model with an integrated social manner in a multi-agent scenario by considering human collision avoidance as well as social comfort distance. At last, experiments on the generated dataset from CrowdNav verify how close our model would act like a human being in the trajectory aspect and also how it could guide the multi-agents by avoiding any collision. Under the same evaluation metrics, CrowdGAIL shows better results compared with classic Social-GAN.
@article{da2022crowdgail, title = {CrowdGAIL: A spatiotemporal aware method for agent navigation}, author = {Da, Longchao and Wei, Hua}, journal = {Electronic Research Archive}, volume = {31}, number = {2}, year = {2022}, }